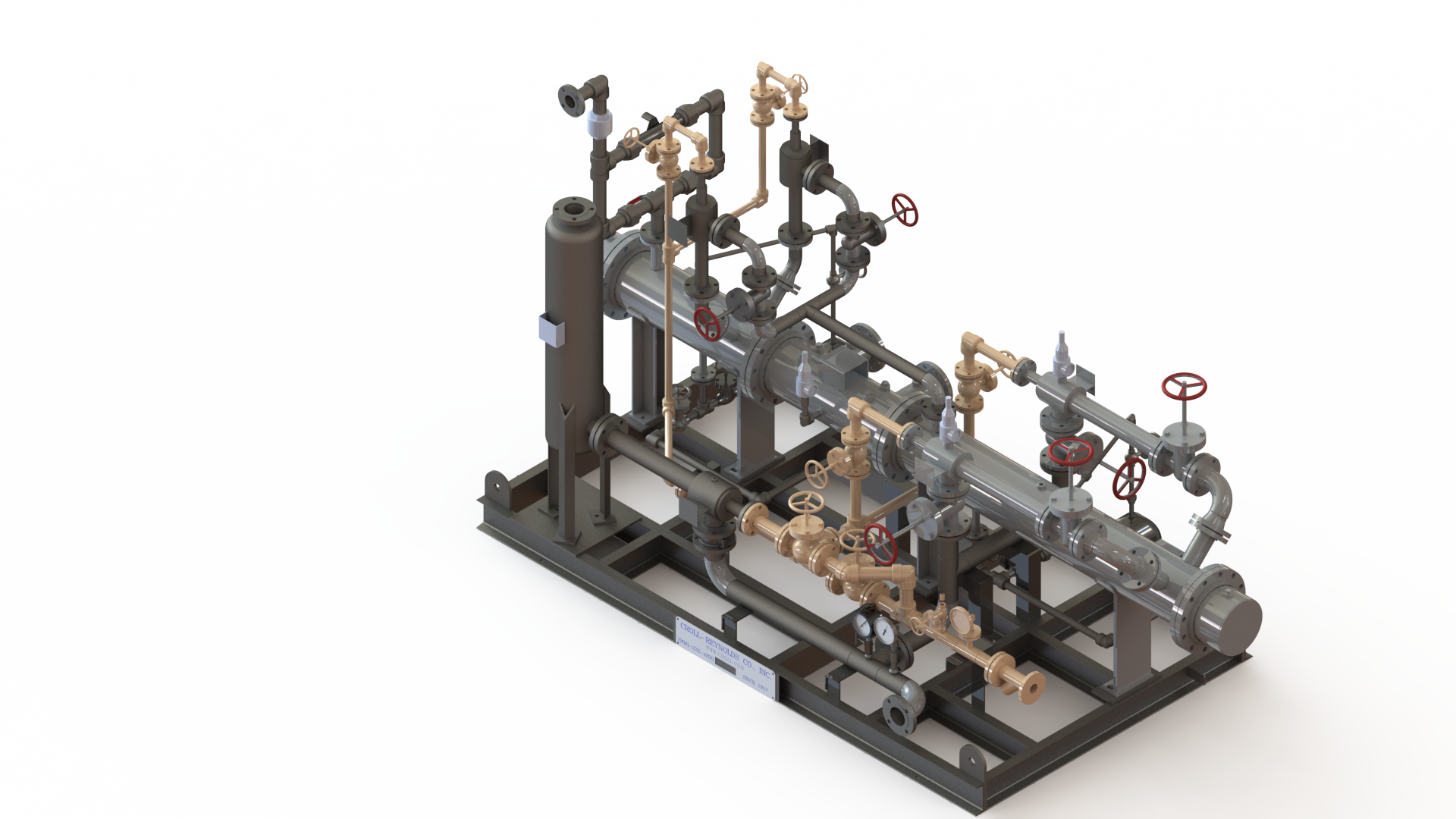
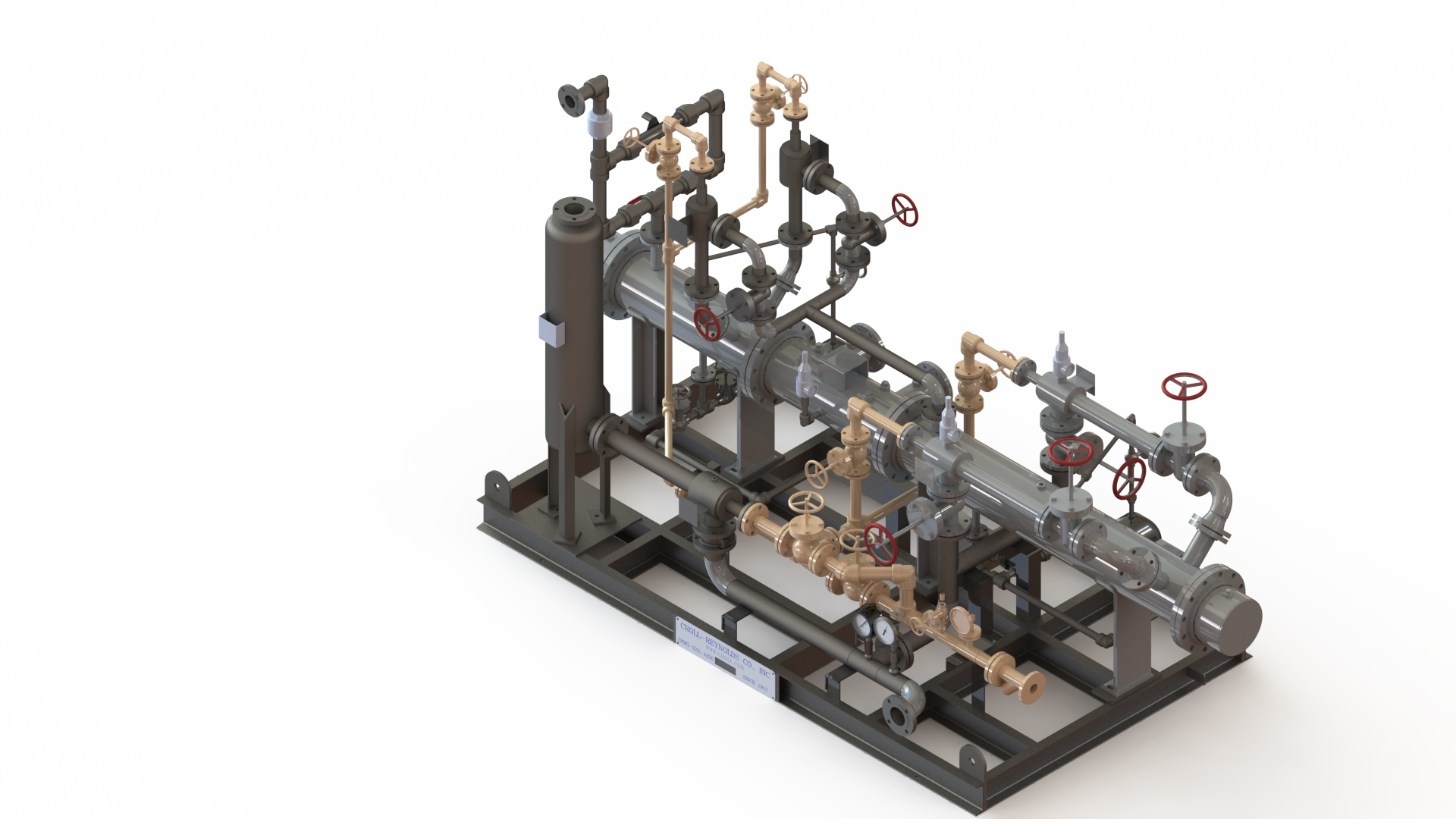
Industrial processes that demand deep, stable vacuum levels often rely on multi-stage configurations to achieve optimal performance. In such applications, efficiency, reliability, and long-term operational stability are essential. Steam Jet Ejector Vacuum Systems have long been recognized as a dependable solution for these requirements, particularly when engineered specifically for multi-stage operation. By applying advanced fluid dynamics principles and application-specific design, these systems deliver consistent vacuum performance while minimizing energy consumption and maintenance demands. At Croll Reynolds, engineering expertise is applied to ensure steam-driven vacuum systems are precisely tailored to meet complex industrial process challenges.
Fundamentals of Steam Jet Ejector Operation
Steam jet ejectors operate by converting the pressure energy of motive steam into velocity through a converging-diverging nozzle. This high-velocity steam creates a low-pressure zone that entrains gases or vapors from the process. The combined flow is then compressed and discharged through a diffuser section. This simple, thermodynamically efficient process eliminates the need for mechanical compression, allowing the system to operate without rotating equipment. Because performance is governed by nozzle geometry and steam conditions rather than mechanical motion, ejectors maintain consistent operation across a wide range of industrial environments.
Role of Multi-Stage Configurations in High Vacuum Applications
Single-stage ejectors are effective for moderate vacuum requirements, but deeper vacuum levels often necessitate multiple stages arranged in series. Each stage incrementally reduces pressure, allowing the system to achieve precise vacuum conditions that would be unattainable with a single ejector. Multi-stage designs enable improved energy utilization by matching each stage to specific pressure ratios, resulting in higher overall efficiency. Proper staging also ensures smooth pressure transitions, reducing instability and enhancing system reliability in demanding applications.
Optimizing Nozzle Design for Maximum Efficiency
The performance of a steam jet ejector system is largely determined by nozzle design. Precise control of throat diameter, expansion angle, and diffuser geometry ensures efficient momentum transfer between steam and entrained gases. In multi-stage systems, each nozzle must be engineered to operate within a defined pressure and flow range. Optimized nozzle geometry minimizes shock losses, improves entrainment ratios, and enhances pressure recovery. This attention to detail ensures that each stage contributes effectively to the overall system performance.
Managing Interstage Condensation and Heat Transfer
In multi-stage steam jet ejector systems, interstage condensers play a critical role in maintaining efficiency. As steam and process vapors pass through each stage, condensation reduces volumetric flow, allowing downstream stages to operate more efficiently. Proper condenser design ensures effective heat transfer while minimizing pressure drop. Efficient removal of condensate also prevents performance degradation and protects downstream ejectors, contributing to stable long-term operation and reduced energy consumption.
Adapting to Variable Process Conditions
Industrial processes rarely operate at constant conditions. Variations in load, temperature, and gas composition can significantly impact vacuum system performance. Multi-stage steam jet ejectors are inherently adaptable, as their operation is not constrained by mechanical speed or electrical controls. By adjusting steam pressure or flow, the system can accommodate changing process demands without compromising stability. This flexibility makes steam jet ejector systems particularly valuable in batch processing, distillation, evaporation, and other variable-load applications.
Material Selection and Mechanical Integrity
Durability is essential for vacuum systems exposed to corrosive gases, high temperatures, and fluctuating pressures. Steam jet ejectors can be fabricated from a wide range of materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and high-alloy metals, to suit specific process environments. Robust construction and simple internal geometry reduce erosion, fouling, and material fatigue. This structural integrity ensures long service life, even in aggressive chemical or high-temperature applications, while maintaining consistent vacuum performance.
Integration into Complex Industrial Systems
Multi-stage steam jet ejector systems are often integrated into larger process units, such as distillation columns, reactors, and evaporators. Their compact footprint and lack of moving parts simplify system layout and reduce installation complexity. Integration is further enhanced by the ability to customize stage arrangement, condenser placement, and discharge configurations. This design flexibility allows engineers to align vacuum system performance precisely with process requirements, improving overall plant efficiency.
Long-Term Efficiency and Total Cost of Ownership
High-efficiency engineering directly impacts the total cost of ownership for vacuum systems. Multi-stage steam jet ejectors reduce operating costs by minimizing energy losses, eliminating mechanical maintenance, and extending service life. Their ability to operate continuously without performance degradation lowers downtime risk and maintenance expenditure. Over time, these factors result in substantial cost savings, making engineered steam jet ejector systems a sound long-term investment for industrial operations.
Conclusion
For industries requiring reliable, high-performance vacuum generation across complex operating conditions, Steam Jet Ejector Vacuum Systems provide a proven and efficient solution. When engineered as multi-stage systems, they deliver precise vacuum control, adaptability, and long-term durability without the limitations of mechanical alternatives. Through application-focused design and deep technical expertise, Croll Reynolds continues to support industrial clients with engineered steam-driven vacuum solutions that enhance efficiency, reliability, and operational value.